Programming With QuickTime VR
| Previous | Chapter Contents | Chapter Top | Next |
A panorama sample atom has an atom type of kQTVRPanoSampleDataAtomType ( 'pdat' ). It describes a single panorama, including track reference indexes of the scene and hot spot tracks and information about the default viewing angles and the source panoramic image.
The structure of a panorama sample atom is defined by the VRPanoSampleAtom data type:
typedef struct VRPanoSampleAtom {
UInt16 majorVersion;
UInt16 minorVersion;
UInt32 imageRefTrackIndex;
UInt32 hotSpotRefTrackIndex;
Float32 minPan;
Float32 maxPan;
Float32 minTilt;
Float32 maxTilt;
Float32 minFieldOfView;
Float32 maxFieldOfView;
Float32 defaultPan;
Float32 defaultTilt;
Float32 defaultFieldOfView;
UInt32 imageSizeX;
UInt32 imageSizeY;
UInt16 imageNumFramesX;
UInt16 imageNumFramesY;
UInt32 hotSpotSizeX;
UInt32 hotSpotSizeY;
UInt16 hotSpotNumFramesX;
UInt16 hotSpotNumFramesY;
UInt32 flags;
UInt32 reserved1;
UInt32 reserved2;
} VRPanoSampleAtom, *VRPanoSampleAtomPtr;
The minimum and maximum values in the panorama sample atom describe the physical limits of the panoramic image. QuickTime VR allows you to set further constraints on what portion of the image a user will see by calling the QTVRSetConstraints routine. You can also preset image constraints by adding constraint atoms to the panorama sample atom container. The three constraint atom types are kQTVRPanConstraintAtomType , kQTVRTiltConstraintAtomType , and kQTVRFOVConstraintAtomType . Each of these atom types share a common structure defined by the VRAngleRangeAtom data type:
typedef struct VRAngleRangeAtom {
Float32 minimumAngle;
Float32 maximumAngle;
} VRAngleRangeAtom, *VRAngleRangeAtomPtr;
The actual panoramic image for a panoramic node is contained in a panorama image track, which is a standard QuickTime video track. The track reference to this track is stored in the imageRefTrackIndex field of the panorama sample atom. The panoramic image can be created in many ways. You can use the panorama stitcher provided by the QuickTime VR Authoring Studio to stitch together several photographs. Alternatively, you can use a graphics rendering application or a panoramic camera.
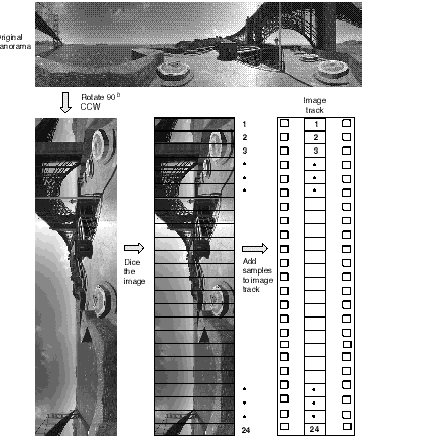
QuickTime VR 2.1 requires the original panoramic image to be rotated 90 degrees counterclockwise. The rotated image must then be diced into smaller frames. Each diced frame is compressed and added to the video track as a video sample. (See Figure 5-4 .) Frames can be compressed using any spatial compressor; temporal compression is not allowed for panoramic image tracks.
A panorama sample atom (which contains information about a single panorama) contains a flag that indicates whether the diced panoramic image is oriented horizontally or vertically. Currently, only vertical orientation is supported. Future versions of QuickTime VR might support horizontal panoramic images.
Figure 4 Creating an image track for a panorama
When a panorama contains hot spots, the movie file contains a hot spot image track, a video track that contains a parallel panorama with the hot spots designated by colored regions. Each diced frame of the hot spot panoramic image must be compressed with a lossless compressor (such as QuickTime's graphics compressor). The dimensions of the hot spot panoramic image are usually the same as those of the image track's panoramic image, but this is not required. The dimensions must, however, have the same aspect ratio as the image track's panoramic image. A hot spot image track should be 8 bits deep.
It's possible to store one or more low-resolution versions of a panoramic image in a movie file; those versions are called low-resolution image tracks. If there is not enough memory at runtime to use the normal image track, QuickTime VR uses a lower resolution image track if one is available. A low-resolution image track contains diced frames just like the higher resolution track, but the reconstructed panoramic image is half the height and half the width of the higher resolution image. The number of diced frames in the lower resolution image track is usually half that in the normal image track.
In QuickTime VR 2.1, the panoramic images in the lower resolution image tracks and the hot spot image tracks, if present, must be rotated 90 degrees counterclockwise (just like images in the panorama image track).
| Previous | Chapter Contents | Chapter Top | Next |